Myofascial release techniques
Myofascial release techniques are treatment methods aimed at releasing tight and restricted tissues through specialized applications on the connective tissue (fascia) surrounding the muscles. Fascia is a thin layer of connective tissue that wraps around muscles and connects different parts of the body. Tension, adhesions, and stiffness in these tissues can lead to pain, restricted movement, and general discomfort. Myofascial release is an effective approach to resolving these issues.
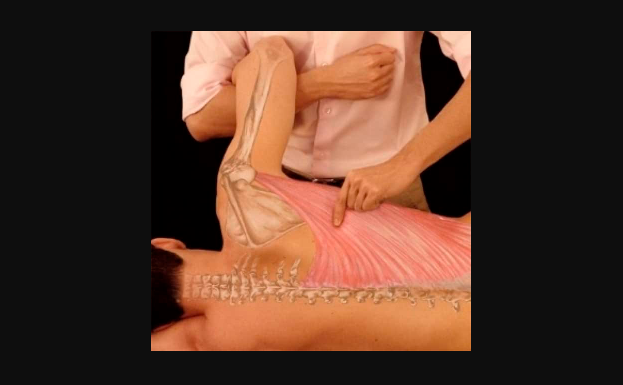
Benefits of Myofascial Release Techniques:
Reduces Muscle Tension: Myofascial release decreases tension in the muscles and connective tissues, promoting relaxation.
Improves Mobility: As tension and adhesions in the fascia are released, joint range of motion increases.
Relieves Pain: When adhesions and tension between muscles are released, muscle spasms and pain are reduced.
Enhances Circulation: Myofascial release increases blood flow, accelerating the healing process.
Improves Posture: By improving the musculoskeletal balance of the body, it supports better posture.
Reduces Injury Risk: Making muscles more flexible and harmonious minimizes the risk of injury.
Myofascial Release Techniques:
This technique targets tension in the fascia. The therapist applies pressure to a specific area of tight tissue and maintains the pressure for a duration. This allows the connective tissue to move more freely and helps resolve tension and adhesions.
Manual Application:
The therapist applies pressure with their hands to specific areas to release the muscles and fascia. Techniques used during the process reduce subcutaneous tension. The application is done slowly and in a controlled manner.
Trigger Point Therapy:
Trigger points in muscles are sensitive spots that cause pain. Special pressure techniques applied to these points relieve tension and spasms in painful areas.
Dynamic Stretching and Slow Manipulation:
The therapist moves slowly while releasing tension in the fascia. This technique helps release the tissue through slow and controlled movements.
Compression and Release:
Direct pressure is applied to the muscle to release tension in the fascial tissue. The compression and release motion reduces tissue tension and improves flexibility.
Deep Tissue Manipulation:
Prolonged pressure applied to deeper tissue layers helps reach and release deep connective tissue structures. This facilitates the release of tight and restricted areas.
Applications of M. Release:
Musculoskeletal Disorders:
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome: Interventions targeting trigger points and muscle tension reduce pain.
- Osteoarthritis and Degeneration: Stiffness and tension in the joints are relieved through m. release.
- Lower Back and Neck Pain: Reducing fascial tension helps the spine move more freely.
Sports and Traumatic Injuries:
- Muscle Tears and Sprains: Pressure and release techniques on injured muscles accelerate healing.
- Stress Fractures: Eliminating muscle imbalances speeds up recovery.
Neurological Conditions:
- Nerve Compressions (Sciatica, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome): Reduces pressure on nerves and relaxes muscles.
Circulatory and Lymphatic System Disorders:
- Varicose Veins and Circulatory Problems: Improves blood flow, reducing swelling and edema in the legs.
- Lymphedema: Promotes lymphatic drainage and reduces fluid accumulation.
Psychological Disorders and Stress:
- Stress and Anxiety: Myofascial release techniques reduce bodily tension and promote emotional relaxation.
- Sleep Disorders: Muscle relaxation may help improve sleep quality.
Who Is It Suitable For?
Myofascial release is particularly beneficial for individuals in the following situations:
- Those experiencing muscle pain and spasms
- Athletes with post-injury tension
- Individuals with chronic posture issues
- Those dealing with psychological stress and muscle tightness
Things to Consider:
Need for a Qualified Therapist: Myofascial release techniques must be applied by a trained professional. Proper and safe application requires the expertise of a qualified therapist.
Pain Management: The treatment should not cause excessive pain during application and should be adapted to the individual’s needs.
Injury Considerations: For severe injuries and trauma, medical approval should always be obtained before performing myofascial release.
One of the world’s leading organizations, APTA (American Physical Therapy Association), provides comprehensive scientific resources on the effectiveness of myofascial release and manual therapy techniques.
